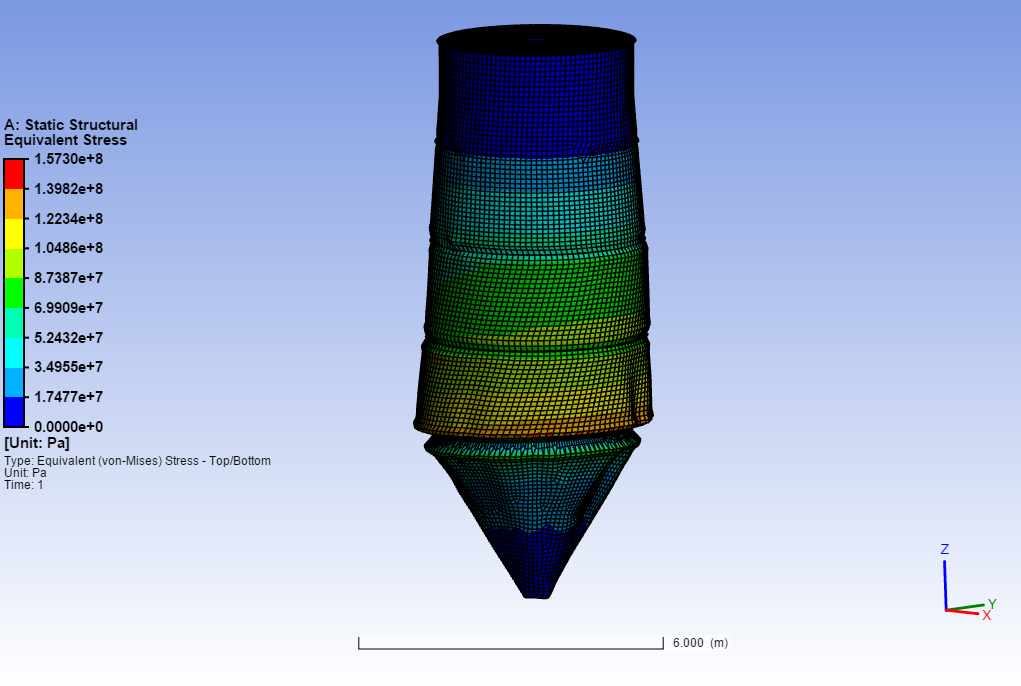
Bulk Silo Loads
I’m typing up this project 5 years after it was done so I may miss a few details. When working on the design of a small-scale cement manufacturing plant, a large capex reduction came from frankensteining equipment from moth-balled factories. We had a fabrication shop so I wondered if it would be possible and cheaper to fabricate the equipment instead. This was a personal project since I needed an excuse to practice more with python coding and running simulations in Ansys, plus a professional engineer would need to sign it off anyways.
I started by extracting repetitive calculations from the Eurocode standards on bulk silo cements (since the South African standards were essentially a copy and I could find them for free online):
actions.py
import math
from math import pi as π
# EN 1991-4 (2006)
class StoredSolidLoad():
def __init__(self, K, μ, d_c, z, γ, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x, ϕ_i):
self.K = K # lateral pressure ratio Table E.1
self.μ = μ # wall friction coefficient Table E.1
self.d_c = d_c # silo inside diameter
self.z = z # depth below equivalent surface
self.γ = γ # unit weight Table E.1
self.h_c = h_c # height of vertical walled segment to solid eq. surface
self.e_f = 0.25 * d_c # maximum eccentricity of surface pile during filling
self.C_op = C_op # patch load solid reference factor Table E.1
self.θ = θ # circumference coordinate of patch load
self.s = (π / 16) * d_c # thickness of patch load zone Eq.5.12
self.β = β # hopper apex half angle
self.h_h = h_h # height from hopper apex to transition
self.x = x # vertical height upwards from hopper apex
self.ϕ_i = ϕ_i # angle of internal friction of stored solid
def f_z0(self): # Janssen characteristic depth
A = (1 / 4) * π * self.d_c**2
U = π * self.d_c
z0 = (1 / (self.K * self.μ)) * (A / U) # Eq.5.5
return z0
def f_Y_Jz(self): # Janssen pressure depth variation
Y_Jz = 1 - math.exp(- self.z / self.f_z0()) # Eq.5.6
return Y_Jz
def f_p_h0(self): # asymptotic horizontal pressure at great depth
p_h0 = self.γ * self.K * self.f_z0() # Eq.5.4
return p_h0
def f_E(self):
E = 2 * (self.e_f / self.d_c) # Eq.5.10
return E
def WallFillingLoad(self):
p_h0 = self.f_p_h0()
Y_Jz = self.f_Y_Jz()
p_hf = p_h0 * Y_Jz # horizontal pressure Eq.5.1
p_wf = self.μ * p_h0 * Y_Jz # wall friction traction Eq.5.2
p_vf = (1 / self.K) * p_h0 * Y_Jz # vertical pressure Eq.5.3
n_zSk = self.μ * p_h0 * (self.z - self.f_z0() * self.f_Y_Jz()) # vertical force in wall per unit length of perimeter
d = {
'p_hf': p_hf,
'p_wf': p_wf,
'p_vf': p_vf,
'n_zSk': n_zSk
}
return d
def FillingPatchLoad(self):
z_p = min(self.f_z0(), 0.5 * self.h_c) # depth of patch zone below eq. surface Eq.5.16
E = self.f_E()
C_pf = 0.21*self.C_op*(1+2*E**2)*(1-math.exp(-1.5*((self.h_c/self.d_c) - 1)))
if C_pf < 0:
C_pf = 0
p_pf = C_pf * self.WallFillingLoad()['p_hf'] # filling patch pressure magnitude Eq.5.8
p_pfs = p_pf * math.cos(self.θ) # circumferential patch pressure variation Eq.5.14
F_pf = (π / 2) * self.s * self.d_c * p_pf # total horizontal force due to filling patch pressure
d = {
'p_pf': p_pf,
'p_pfs': p_pfs,
'F_pf': F_pf,
'z_p': z_p
}
return d
def WallDischargeLoad(self):
C_h = 1.15 # horizontal discharge factor Eq.5.21
C_w = 1.10 # wall friction discharge factor Eq.5.22
p_he = C_h * self.WallFillingLoad()['p_hf'] # Eq.5.18
p_we = C_w * self.WallFillingLoad()['p_wf'] # Eq.5.19
n_zSk = C_w * self.WallFillingLoad()['n_zSk']
d = {
'p_he': p_he,
'p_we': p_we,
'n_zSk': n_zSk
}
return d
def DischargePatchLoad(self):
z_p = min(self.f_z0(), 0.5 * self.h_c) # depth of patch zone below eq. surface Eq.5.16
E = self.f_E()
C_pe = 0.42*self.C_op*(1+2*E**2)*(1-math.exp(-1.5*((self.h_c/self.d_c) - 1))) # Eq.5.28
p_pe = C_pe * self.WallDischargeLoad()['p_he'] # p_he is local value at height that patch load is applied Eq.5.27
p_pes = p_pe * math.cos(self.θ)
F_pe = (π / 2) * self.s * self.d_c * p_pe # total horizontal force due to filling patch pressure
d = {
'p_pe': p_pe,
'p_pes': p_pes,
'F_pe': F_pe,
'z_p': z_p
}
return d
def HopperFillingLoad(self):
if (math.tan(self.β) > (1-self.K)/(2 * self.μ)):
print("Hopper category is shallow and results are not valid!")
if self.z != self.h_c:
print("z is not equal to the transition and results are not valid!")
C_b = 1.0 # bottom load magnifier Eq.6.3
p_vft = C_b * self.WallFillingLoad()['p_vf']
b = 0.2 # empirical coefficient §6.3.2.
F_f = 1 - b / (1 + math.tan(self.β) / (self.μ))
S = 2 # value for conical hoppers Eq.6.9
n = S * (1 - b) * self.μ / math.tan(self.β) # n = S*(F_f * self.μ / math.tan(self.β) + F_f) - 2
p_v = ((self.γ * self.h_h )/(n-1))*((self.x/self.h_h)-(self.x/self.h_h)**n)+p_vft*(self.x/self.h_h)**n # mean vertical stress in solid at height x above apex
p_nf = F_f * p_v # normal pressure in hopper during filling and full load
p_tf = self.μ * F_f * p_v # frictional traction in hopper at x along hopper wall
d = {
'p_v': p_v,
'p_nf': p_nf,
'p_tf': p_tf
}
return d
def HopperDischargeLoad(self):
if (math.tan(self.β) > (1-self.K)/(2 * self.μ)):
print("Hopper category is shallow and results are not valid!")
if self.z != self.h_c:
print("z is not equal to the transition and results are not valid!")
C_b = 1.0 # bottom load magnifier Eq.6.3
p_vft = C_b * self.WallFillingLoad()['p_vf']
ϕ_wh = math.atan(self.μ)
ε = ϕ_wh + math.asin(math.sin(ϕ_wh) / math.sin(self.ϕ_i))
F_e = (1 + math.sin(self.ϕ_i) * math.cos(ε)) / (1 - math.sin(self.ϕ_i) * math.cos(2 * self.β + ε))
S = 2 # value for conical hoppers Eq.6.9
n = S*(F_e * self.μ / math.tan(self.β) + F_e) - 2
p_v = ((self.γ * self.h_h )/(n-1))*((self.x/self.h_h)-(self.x/self.h_h)**n)+p_vft*(self.x/self.h_h)**n # mean vertical stress in solid at height x above apex
p_ne = F_e * p_v # normal pressure in hopper during filling and full load
p_te = self.μ * F_e * p_v # frictional traction in hopper at x along hopper wall
d = {
'p_v': p_v,
'p_ne': p_ne,
'p_te': p_te
}
return dgeometry.py
import math
from math import pi as π
class SiloGeom():
def __init__(self, Mg, d_c, γ_l, γ_u, β, ψ):
self.F_g = Mg * 9.81 # force of stored solid (tonnes to kN)
self.d_c = d_c # silo inside diameter
self.r_c = d_c / 2 # silo inside diameter
self.γ_l = γ_l # unit weight lower value
self.γ_u = γ_u # unit weight upper value
self.β = β # hopper apex half angle
self.ψ = ψ # angle of repose of stored solid
self.A = (1/4) * π * d_c**2 # cross sectional area of silo
def silo_dims(self):
#Hopper
h_h = self.r_c / math.tan(self.β) # hopper height
V_h = (1/3) * π * h_h * self.r_c**2 # hopper volume
#Repose
h_r = self.r_c * math.tan(self.ψ) # height of pile on top of silo due to internal friction
V_r = (1/3) * π * h_r * self.r_c**2 # volume of pile
V_t = self.F_g / self.γ_l # total min volume of silo
#Silo vertical wall
V_s = V_t - V_h - V_r
h_s = V_s / self.A
d = {
'h_h': h_h,
'V_h': V_h,
'h_r': h_r,
'V_r': V_r,
'h_s': h_s,
'V_s': V_s
}
return d
def solid_dims(self):
V_t1 = self.F_g / self.γ_u # total min volume of solid
V_t2 = V_t1 - self.silo_dims()['V_h'] # total solid volume minus hopper volume
V_t3 = V_t2 - self.silo_dims()['V_s'] # remaining solid volume in the repose volume
if V_t3 < 0: # stored solid does not pass vertical walls
h_b = self.silo_dims()['h_h'] + (V_t2 / self.A) #height of solid surface from hopper apex
return h_bsilo.py
from geometry import SiloGeom
from actions import StoredSolidLoad
from math import pi as π
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# inputs
Mg = 150
d_c = 3.82
γ_l = 8.0
γ_u = 16.0
β = 30*(π/180)
ψ_u = 41*(π/180)
K_l = 0.52 / 1.20 # cement
K_u = 0.54 * 1.20 # cement
μ_l = 0.46 / 1.70 # cement
μ_u = 0.46 * 1.70 # cement
C_op = 0.4 # cement
θ = 0
ϕ_l = (30 / 1.22) * ((π/180)) # cement
ϕ_u = (30 * 1.22) * ((π/180)) # cement
# calculate silo geometry
geom = SiloGeom(Mg, d_c, γ_l, γ_u, β, ψ_u) # Mg, d_c, γ_l, γ_u, β, ψ
h_h = geom.silo_dims()['h_h'] # height of hopper apex to transition
h_b = geom.solid_dims() # height of hopper apex to to eq. surface
h_c = h_b - h_h # height of transition to solid eq. surface
z = h_c
x = h_h
x_i_lst = np.linspace(0, h_h, 10) # x coordinates for plotting graph
z_i_lst = np.linspace(0, h_c, 10) # z coordinates for plotting graph
# wall filling loads
wall_max_pn_f = []
wall_max_pft_f = []
wall_max_pv_f = []
# wall discharge loads
wall_max_pn_e = []
wall_max_pft_e = []
wall_max_pv_e = []
# hopper filling loads
hopper_max_pv_f = []
hopper_max_pn_f = []
hopper_max_pt_f = []
# hopper discharge loads
hopper_max_pv_e = []
hopper_max_pn_e = []
hopper_max_pt_e = []
for idz , z_i in enumerate(z_i_lst):
wall_max_pn_f.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_u, μ_l, d_c, z_i, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x, ϕ_l).WallFillingLoad()['p_hf'])
wall_max_pft_f.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_u, μ_u, d_c, z_i, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x, ϕ_l).WallFillingLoad()['p_wf'])
wall_max_pv_f.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z_i, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x, ϕ_l).WallFillingLoad()['p_vf'])
wall_max_pn_e.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_u, μ_l, d_c, z_i, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x, ϕ_l).WallDischargeLoad()['p_he'])
wall_max_pft_e.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_u, μ_u, d_c, z_i, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x, ϕ_l).WallDischargeLoad()['p_we'])
wall_max_pv_e.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z_i, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x, ϕ_l).WallFillingLoad()['p_vf'])
for idx, x_i in enumerate(x_i_lst):
hopper_max_pv_f.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x_i, ϕ_l).HopperFillingLoad()['p_v'])
hopper_max_pn_f.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x_i, ϕ_l).HopperFillingLoad()['p_nf'])
hopper_max_pt_f.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x_i, ϕ_l).HopperFillingLoad()['p_tf'])
hopper_max_pv_e.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x_i, ϕ_u).HopperDischargeLoad()['p_v'])
hopper_max_pn_e.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x_i, ϕ_u).HopperDischargeLoad()['p_ne'])
hopper_max_pt_e.append(StoredSolidLoad(K_l, μ_l, d_c, z, γ_u, h_c, C_op, θ, β, h_h, x_i, ϕ_u).HopperDischargeLoad()['p_te'])
# rearrange lists to use common coordinates
z_p_lst_i = z_i_lst + h_h
z_p_lst = np.concatenate((x_i_lst, z_p_lst_i))
print(z_p_lst)
# rearrange filling pressures for plot1
plot_max_pn_f = hopper_max_pn_f
plot_max_pn_f.extend(wall_max_pn_f[::-1])
plot_max_pft_f = hopper_max_pt_f
plot_max_pft_f.extend(wall_max_pft_f[::-1])
plot_max_pv_f = hopper_max_pv_f
plot_max_pv_f.extend(wall_max_pv_f[::-1])
plot1 = plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(plot_max_pn_f, z_p_lst, label="p_nf")
plt.plot(plot_max_pft_f, z_p_lst, label="p_tf")
plt.plot(plot_max_pv_f, z_p_lst, label="p_vf")
plt.xlabel('Pressure (kN/m3) (kPa)')
plt.ylabel('Height above hopper apex (m)')
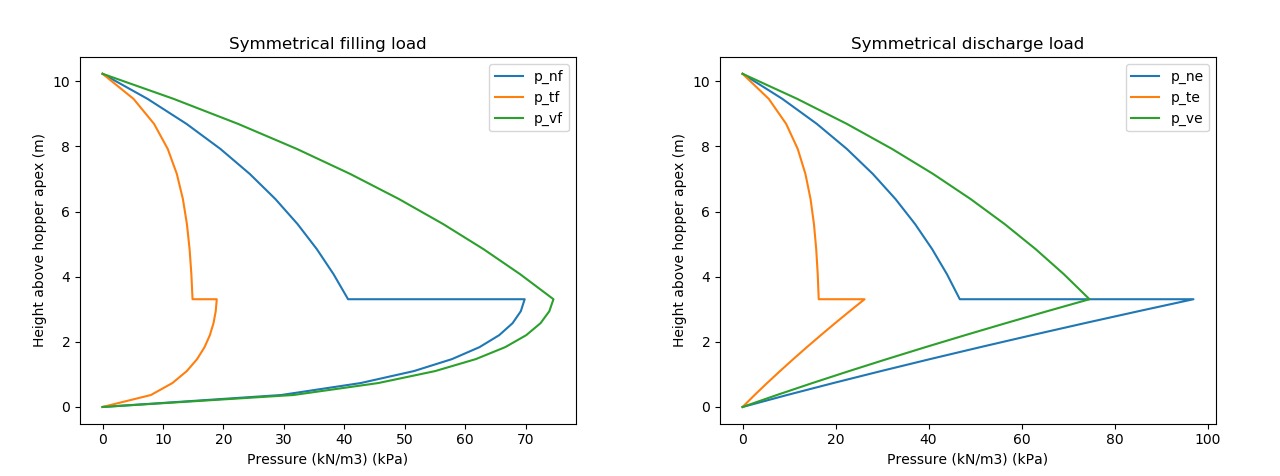
plt.title('Symmetrical filling load')
plt.legend()
# rearrange discharge pressures for plot2
plot_max_pn_e = hopper_max_pn_e
plot_max_pn_e.extend(wall_max_pn_e[::-1])
plot_max_pft_e = hopper_max_pt_e
plot_max_pft_e.extend(wall_max_pft_e[::-1])
plot_max_pv_e = hopper_max_pv_e
plot_max_pv_e.extend(wall_max_pv_e[::-1])
plot2 = plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(plot_max_pn_e, z_p_lst, label="p_ne")
plt.plot(plot_max_pft_e, z_p_lst, label="p_te")
plt.plot(plot_max_pv_e, z_p_lst, label="p_ve")
plt.xlabel('Pressure (kN/m3) (kPa)')
plt.ylabel('Height above hopper apex (m)')
plt.title('Symmetrical discharge load')
plt.legend()
plt.show()This produced the below plots:
FEA Simulations
There are several types of forces we need to implement from the simulations, using the above calculated loads, such as:
- Wall normal forces of the bulk solids pushes outwards
- Wall friction forces from filling/discharging1
- Variable hopper normal forces
- Forces from the fixed supports
3mm Wall Thickness
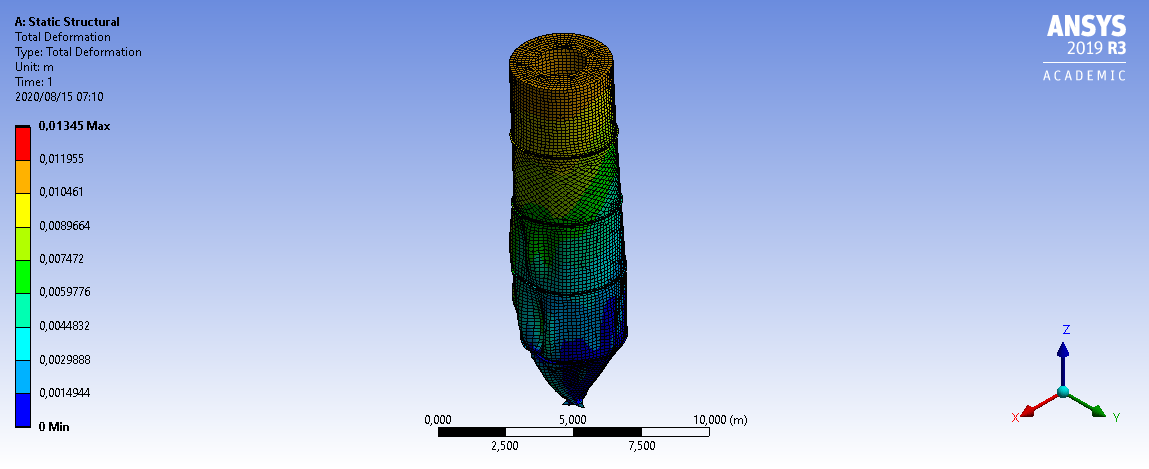
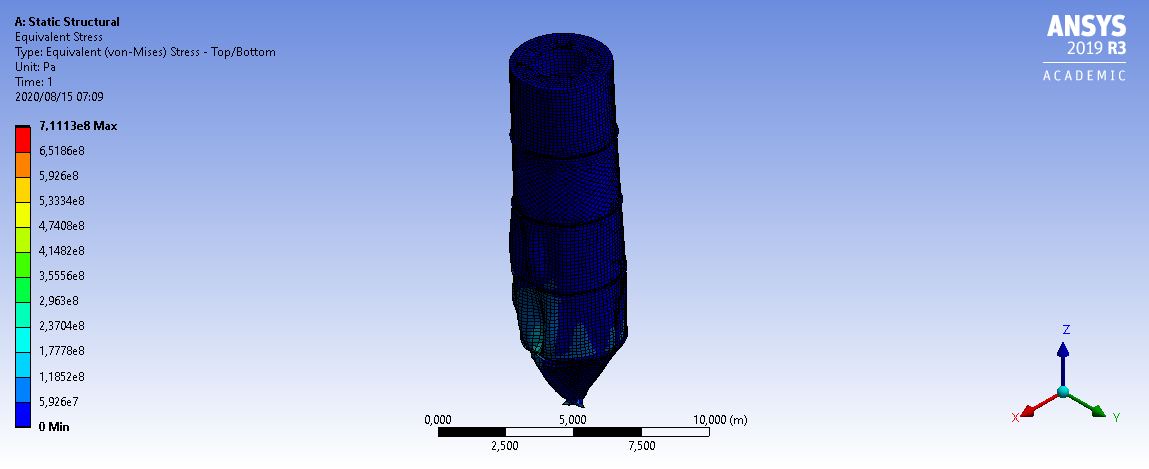
6mm Wall Thickness
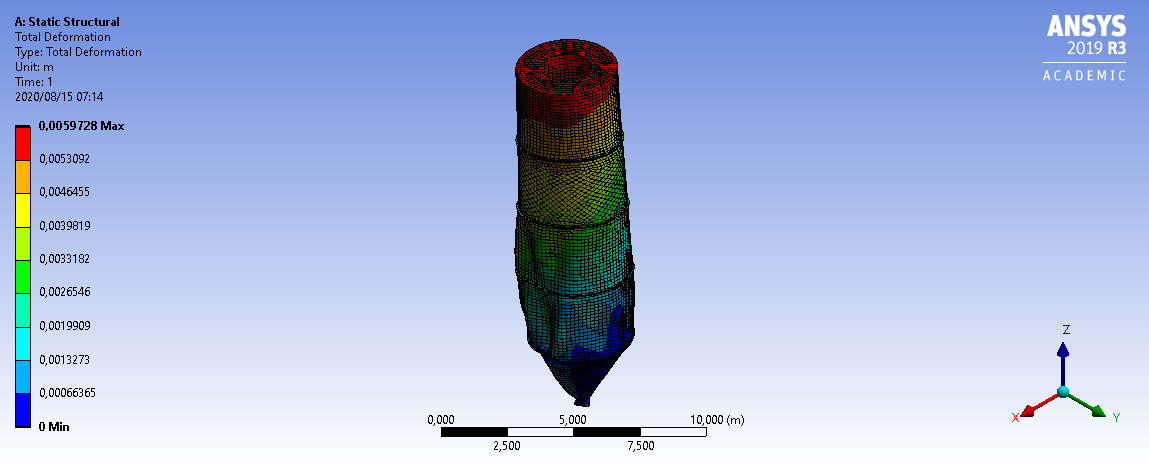
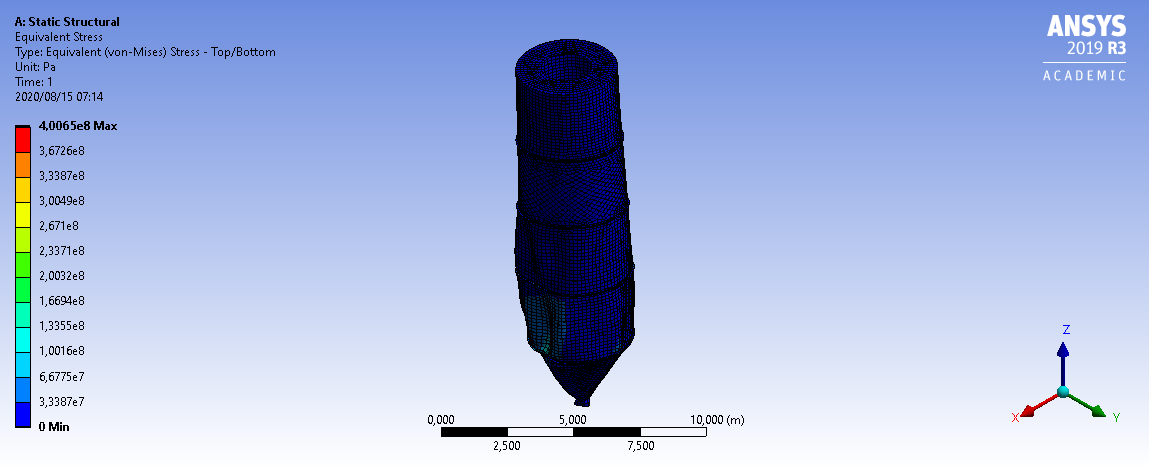
3D Model
Footnotes
-
If I remember correctly, the most greatest forces occur during discharge due to the friction forces of the bulk solids. This aligns with the values calculated and shown in the plots. ↩